Why Are Babies Not Allowed To Eat Honey?
You shouldn’t give babies honey because it contains a bacterium that can be very dangerous, if not fatal, for children under one year of age.

You are wondering why babies are not allowed to eat honey ? Honey is a nutritious and healthy food that has a distinctive taste and sweetens life. Parents and grandparents also like to pamper babies with a little honey on the pacifier, but we now know that this can be dangerous. Under no circumstances should children under twelve months eat honey. Then find out why.
Honey and botulism: why babies are not allowed to eat honey!
We humans have been consuming honey for thousands of years. It is considered to be one of the most natural and noble foods. Its benefits are many and well known. From ancient Egypt to the present day , honey has always been an ingredient in all kinds of recipes, providing nutrients and sweeteners in a natural way.
As a natural product , honey contains a bacterium, Clostridium botulinum , which can be very dangerous for babies under one year of age.
The reason is simple: the intestinal flora of the smallest ones is not yet sufficiently developed so that the spores of this bacterium can multiply in their intestines and release botulinum toxin. This is considered to be one of the deadliest known substances.
This is what is known as infant botulism, a form of botulism that primarily affects children under twelve months and can be fatal. Children over one year of age already have better defenses and are able to prevent this bacterium from multiplying.
Infant botulism
Clostridium botulinum is a naturally occurring bacillus that is found in all types of food, regardless of whether they are of vegetable or animal origin.
This bacterium organizes itself in spores and can remain inactive until it finds the ideal conditions for reproduction and growth. It is mainly found in home-made preserves, prefers low-oxygen environments and generally does not tolerate acidic substances.
In addition , it cannot grow in solutions with high concentrations of sugar. For this reason, it usually remains inactive, especially in honey, and waits for the ideal conditions for its growth.
So when honey is ingested by an infant under twelve months of age , the sugar in the nectar is diluted in its still low-acid gastric juice, where there is also little oxygen.
The bacillus therefore finds ideal conditions for reproduction and growth in this medium and releases botulinum toxin. It then reaches the neuromuscular endplates through the bloodstream, which can lead to botulism in the infant. This is a highly dangerous condition that requires immediate hospitalization.
Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Infant botulism affects the nervous system so it can have a variety of symptoms. They usually appear 12 to 48 hours after contact with the bacteria. The most common are:
- Slow breathing or breathlessness
- constipation
- General weakness
- Soft crying
- lethargy
- Reduced arc reflex
- Double or blurred vision
- Dry mouth
- Sagging eyelids
- General weakness
- Slow food intake
- In extreme cases: paralysis of the upper body, arms and legs or paralysis of the respiratory system
Diagnosis and treatment
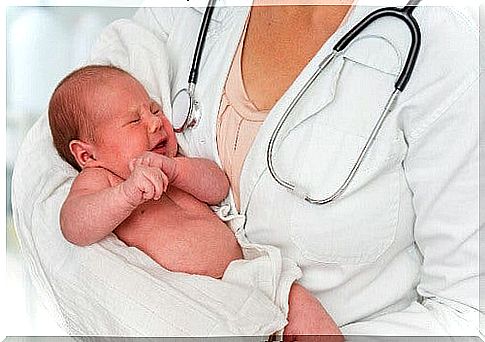
Based on the symptoms described by the parents, the pediatrician will assess whether the child has botulism. To confirm this , all that is needed is a stool analysis of the baby to check for the presence of botulinum toxin. Infant botulism requires immediate hospitalization.
As mentioned earlier, this affects the nervous system and can lead to respiratory failure. Because of this, it is necessary that the baby is under constant observation in the hospital.
The success of the treatment always depends on the early detection and the timely administration of the botulism antiserum. In the most severe cases, the child may even need artificial respiration or intravenous feeding.
In any case, infant botulism usually disappears after a few weeks or months. Only in the most extreme cases can the effects of the toxin cause death from respiratory failure.
Can Only Honey Cause Infant Botulism?
It’s not just honey that can cause infant botulism. As mentioned earlier, the bacterium responsible for this disease is widespread in nature. Hence, it is quite difficult to identify the source of the spores.
In fact, the botulinum bacterium can even be found in the ground or in dust and carried through the air that babies breathe. Therefore, it should be avoided that infants are in an environment with a lot of dust, or where earthworks are carried out.
Due to the severity of botulism and the difficulty in getting rid of the bacteria, it is necessary to watch out for any outbreaks of this bacillus to avoid contagion and possible epidemics.
In this context, the WHO (World Health Organization) ensures safety and promotes the monitoring, detection, risk assessment and containment of the disease.
Even if outbreaks occur rarely of botulism, they are always a threat to public health and it needs to be determined quickly whether the outbreak is natural, accidental or deliberate. In this way new cases can be prevented and those affected can be treated effectively.
advices

Since there is no vaccine against the bacteria responsible for botulism, it is best to prevent. Pediatricians recommend the following:
- Never give honey to children under twelve months of age.
- Like honey, corn syrup can contain these bacteria and should therefore not be given to babies.
- Avoid contact with dirt or dust that could be contaminated.
- Boil the food stored at home (especially homemade canned food).
- Pay attention to adequate hygiene.
This is why babies shouldn’t eat honey
Even if it is a sweet food with important nutrients, it increases the risk of botulism in children. This is because their immune systems are not yet sufficiently developed and therefore cannot fight the microorganism that causes this disease.
However, one must be vigilant and remember that it is not just honey that causes botulism. With proper hygiene and advice from experts, you can protect the little ones from the risk.